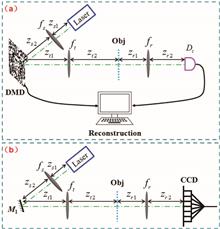
A new architecture, naked-eye ghost imaging via photoelectric feedback, is developed that avoids computer algorithm processing. Instead, the proposed scheme uses a photoelectric feedback loop to first realize the correlation (multiplication) process of the traditional ghost imaging system. Then, the vision persistence effect of the naked eye is exploited to implement the integral process and to generate negative images. Two kinds of feedback circuits, the digital circuit and the analog circuit, are presented that can achieve a feedback operation. Based on this design, high-contrast real-time imaging of moving objects is obtained via a special pattern-scanning architecture on a low-speed light-modulation mask.
The performances of ghost imaging and conventional imaging in photon shot noise cases are investigated. We define an imaging signal-to-noise ratio called SNRtran where only the object’s transmission region is used to evaluate the imaging quality and it can be applied to ghost imaging (GI) with any random pattern. Both the values SNRGItran of GI and SNRCItran of conventional imaging in photon shot noise cases are deduced from a simple statistical analysis. The analytical results, which are backed up by numerical simulations, demonstrate that the value SNRGItran is related to the ratio between the object’s transmission area Ao and the number density of photons illuminating the object plane Io, which is similar to the theoretical results based on the first principle of GI with a Gaussian speckle field deduced by B. I. Erkmen and J. H. Shapiro [in Adv. Opt. Photonics 2, 405–450 (2010)]. In addition, we also show that the value SNRCItran will be larger than SNRGItran when Ao is beyond a threshold value.
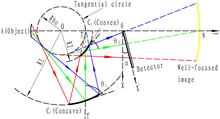
An aberration-free imaging technique was used to design a double-spherically bent crystal spectrometer with high energy and spatial resolutions to ensure that the individual spectral lines are represented as perfectly straight lines on the detector. After obtaining the matched parameters of the two crystals via geometry-based optimization, an alignment method was employed to allow the spacing between the crystals and the detector to be coupled with the source. The working principle of this spectrum-measuring scheme was evaluated using a Cu X-ray tube. High-quality spectra with energy resolutions (E/ΔE) of approximately 3577 were obtained for a relatively large source size.
The resolution of a conventional imaging system based on first-order field correlation can be directly obtained from the optical transfer function. However, it is challenging to determine the resolution of an imaging system through random media, including imaging through scattering media and imaging through randomly inhomogeneous media, since the point-to-point correspondence between the object and the image plane in these systems cannot be established by the first-order field correlation anymore. In this Letter, from the perspective of ghost imaging, we demonstrate for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, that the point-to-point correspondence in these imaging systems can be quantitatively recovered from the second-order correlation of light fields, and the imaging capability, such as resolution, of such imaging schemes can thus be derived by analyzing second-order autocorrelation of the optical transfer function. Based on this theoretical analysis, we propose a lensless Wiener–Khinchin telescope based on second-order spatial autocorrelation of thermal light, which can acquire the image of an object by a snapshot via using a spatial random phase modulator. As an incoherent imaging approach illuminated by thermal light, the lensless Wiener–Khinchin telescope can be applied in many fields such as X-ray astronomical observations.
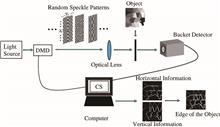
In this Letter, we propose an advanced framework of ghost edge imaging, named compressed ghost edge imaging (CGEI). In the scheme, a set of structured speckle patterns with pixel shifting illuminate on an unknown object. The output is collected by a bucket detector without any spatial resolution. By using a compressed sensing algorithm, we obtain horizontal and vertical edge information of the unknown object with the bucket detector detection results and the known structured speckle patterns. The edge is finally constructed via two-dimensional edge information. The experimental and numerical simulations results show that the proposed scheme has a higher quality and reduces the number of measurements, in comparison with the existing edge detection schemes based on ghost imaging.
The precise alignment of a high-performance telescope is a key factor to ensure the imaging quality. However, for telescopes with a wide field of view, the images are sometimes under-sampled. To study the effects of under-sampled images on the precision of telescope alignment, numerical simulations are implemented with the stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm. The results show that the alignment program can converge stably and quickly. However, with the reduction of the full width at half-maximum of images, the relative residual errors increase from 9.5% to 19.5%, and the wavefront errors raise from 0.0972λ to 0.1074λ, indicating that the accuracy of the alignment decreases.
Optical frequency combs, which are generated by the cascade of a phase modulator and a Mach–Zehnder intensity modulator, are used as a polychromatic signal source in the terahertz imaging system to improve imaging quality. The interference effect caused by the monochromatic wave has been greatly suppressed. The required optical power in the presented system is as low as ~30% of that in the system using the Er-doped fiber amplifier as a source, which can reduce cost and protect photodiodes from damage. This work provides an effective, low power consumption, low cost, and easy way to realize terahertz imaging with high quality and can be used in future security inspections.
A frequency-degenerate cavity (FDC) is the resonator that the ratio of transverse and longitudinal mode frequency spacings is a simple rational number. When an optical resonator is close to the FDC, transverse-mode-locking (TML) takes place with drastic changes of laser mode. We report for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, the multi-frequency emission and spectral modulation effects coupled with TML in FDC. The Yb:CaGdAlO4 (Yb:CALGO) crystal with large gain bandwidth was used as a gain medium in an off-axis-pumped hemispherical FDC for realizing broadband emission. Interestingly, the spectrum can transform from a single smooth packet shape to a multi-peak structure; meanwhile, the transverse pattern accordingly transforms into some exotic wave-packet profiles through controlling off-axis displacement in a special degenerate state.
Subtractive imaging is used to suppress the axial sidelobes and improve the axial resolution of 4pi microscopy with a higher-order radially polarized (RP) Laguerre–Gaussian (LG) beam. A solid-shaped point spread function (PSF) and a doughnut-shaped PSF with a dark spot along the optical axis are generated by tightly focusing a higher-order RP-LG beam and a modulated circularly polarized beam, respectively. By subtracting the two images obtained with those two different PSFs, the axial sidelobes of the subtracted PSF are reduced from 37% to about 10% of the main lobe, and the axial resolution is increased from 0.21λ to 0.15λ.
We develop a source and mask co-optimization framework incorporating the minimization of edge placement error (EPE) and process variability band (PV Band) into the cost function to compensate simultaneously for the image distortion and the increasingly pronounced lithographic process conditions. Explicit differentiable functions of the EPE and the PV Band are presented, and adaptive gradient methods are applied to break symmetry to escape suboptimal local minima. Dependence on the initial mask conditions is also investigated. Simulation results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed source and mask optimization approach in pattern fidelity improvement, process robustness enhancement, and almost unaffected performance with random initial masks.
Dispersed fringe sensors are a promising approach for sensing the large-scale physical step between adjacent segments with acceptable accuracy. However, the nature of dispersion in a dispersed fringe sensor leads to the ideal dispersed fringe pattern becoming vulnerable to noise, particularly at low light levels. A reliable merit-function-based algorithm with an active actuation is introduced here. The feasibility of our algorithm is numerically demonstrated, and Monte Carlo experiments for different signal-to-noise ratios are conducted to assess its robustness. The results show that the method is valid even when the signal-to-noise ratio is as low as 1.
In our Letter, two kinds of handwriting traces, colored and colorless, are studied by means of reflectance transformation imaging. The illumination direction and rendering mode can be changed alternatively to obtain two-dimensional and three-dimensional details of the traces that are not recognized easily by naked eyes. Furthermore, an objective evaluation method without reference is applied to evaluate the reconstructed images, which provides a basis for setting the illumination direction and rendering mode. Therefore, the handwriting trace information including the written content, the writing features, and the stroke order features can be obtained objectively and accurately.
This Letter proposes a snapshot imaging spectrometer, which obtains the spectral information and spatial information in one “shot”. The device proposed can achieve the data cube size of 21×29×40 in the waveband of 400–800 nm. The core element of this system is the microlens array, which contains 60×60 microlenses in a square arrangement, each microlens has an aperture of 125 μm×125 μm, and the F number is 15. The microlens array is mounted in a rotation mount, which provides 360° of rotation around the optical axis to maximize the spectral resolution. The final resolution of the system is about 10 nm.
Detecting and tracking multiple targets simultaneously for space-based surveillance requires multiple cameras, which leads to a large system volume and weight. To address this problem, we propose a wide-field detection and tracking system using the segmented planar imaging detector for electro-optical reconnaissance. This study realizes two operating modes by changing the working paired lenslets and corresponding waveguide arrays: a detection mode and a tracking mode. A model system was simulated and evaluated using the peak signal-to-noise ratio method. The simulation results indicate that the detection and tracking system can realize wide-field detection and narrow-field, multi-target, high-resolution tracking without moving parts.
Traditional one-way imaging methods become invalid when a target object is completely hidden behind scattering media. In this case, it has been much more challenging, since the light wave is distorted twice. To solve this problem, we propose an imaging method, so-called round-trip imaging, based on the optical transmission matrix of the scattering medium. We show that the object can be recovered directly from the distorted output wave, where no scanning is required during the imaging process. We predict that this method might improve the imaging speed and have potential application for real-time imaging.
The work proposes a three-laser-beam streak tube imaging lidar system. Besides the main measuring laser beam, the second beam is used to decrease the error of time synchronization. The third beam has n+0.5 pixels’ difference compared to the main measuring beam on a CCD, and it is used to correct the error caused by CCD discrete sampling. A three-dimensional (3D) imaging experiment using this scheme is carried out with time bin size of 0.066 ns (i.e., corresponding to a distance of 9.9 mm). An image of a 3D model is obtained with the depth resolution of <2 mm, which corresponds to ~0.2 pixel.
Enhanced quantitative X-ray phase-contrast (QXPC) imaging is implemented with a Foucault knife-edge array filter (FKAF), which is a real differential spatial filter. The intensities of Foucault differential filtering (FDF) are acquired according to the linear translation of the FKAF along the axes. The FDF using the FKAF scheme for obtaining the QXPC images is demonstrated by a stereoscopic rendering of the quantitative phase images of the tail fin of an anchovy containing soft and hard components in specimen. FDF is a noninterferometric quantitative phase-imaging method that depicts quantitative phase images and renders stereoscopic images.
In this Letter, we propose a three-dimensional (3D) free view reconstruction technique in axially distributed image sensing (ADS). In typical integral imaging, free view reconstructed images can be obtained by tilting all elemental images or tilting the reconstruction plane due to large lateral perspectives for 3D objects. In conventional ADS, the reconstructed images at only a front view can be generated since the sensor is moved along with its optical axis so that it has small lateral perspectives for 3D objects. However, the reconstructed 3D images at any viewing point may be obtained because the virtual viewing camera may capture these slightly different perspectives for 3D objects. Therefore, in this Letter, we employ the virtual viewing camera to visualize the 3D images at the arbitrary viewing point. To support our proposed method, we show the experimental results.
Transporting information is one of the important functions of photons and is also the essential duty of information science. Here, we realize multiple imaging by detecting photons with changeable wavelengths based on time-resolved correlation measurements. In our system, information from multiple objects can be transported. During this process, the wavelength of the photons illuminating the objects is different from the wavelength of the photons detected by the detectors. More importantly, the wavelength of the photons that are utilized to record images can also be changed to match the sensitive range of the used detectors. In our experiment, images of the objects are reconstructed clearly by detecting the photons at wavelengths of 650, 810, and 1064 nm, respectively. These properties should have potential applications in information science.
We develop an improved region growing method to realize automatic retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cell segmentation for photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) imaging. The minimum bounding rectangle of the segmented region is used in this method to dynamically update the growing threshold for optimal segmentation. Phantom images and PAM imaging results of normal porcine RPE are applied to demonstrate the effectiveness of the segmentation. The method realizes accurate segmentation of RPE cells and also provides the basis for quantitative analysis of cell features such as cell area and component content, which can have potential applications in studying RPE cell functions for PAM imaging.
In this Letter, we propose an on-line inspection method based on a plenoptic camera to detect and locate flaws of optics. Specifically, due to the extended depth of field of the plenoptic camera, a series of optics can be inspected efficiently and simultaneously. Moreover, the depth estimation capability of the plenoptic camera allows for locating flaws while detecting them. Besides, the detection and location can be implemented with a single snapshot of the plenoptic camera. Consequently, this method provides us with the opportunity to reduce the cost of time and labor of inspection and remove the flaw optics, which may lead to performance degradation of optical systems.
In this Letter, we report a Golay3 sparse-aperture telescope newly built in the Key Laboratory of Optical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences and present the experimental results of enhanced resolution. The telescope consisting of 3 collector telescopes of 127 mm diameter can achieve a theoretical resolution corresponding to a monolithic aperture of 245 mm diameter. It is shown by the experimental results that the resolution is improved to 3.33 μrad with respect to the diffraction limit of 6.07 μrad for a single aperture using the Rayleigh criteria at 632 nm. The compact optical configuration and cophasing approach are also described.
A bimorph deformable mirror (DM) with a large stroke of more than 30 μm using 35 actuators is presented and characterized for an adaptive optics (AO) confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope application. Facilitated with a Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor, the bimorph DM-based AO operates closed-loop AO corrections for human eyes and reduces wavefront aberrations in most eyes to below 0.1 μm rms. Results from living eyes, including one exhibiting ~5D of myopia and ~2D of astigmatism along with notable high-order aberrations, reveal a practical efficient aberration correction and demonstrate a great benefit for retina imaging, including improving resolution, increasing brightness, and enhancing the contrast of images.
Single-pixel cameras, which employ either structured illumination or image modulation and compressive sensing algorithms, provide an alternative approach to imaging in scenarios where the use of a detector array is restricted or difficult because of cost or technological constraints. In this work, we present a robust imaging method based on compressive imaging that sets two thresholds to select the measurement data for image reconstruction. The experimental and numerical simulation results show that the proposed double-threshold compressive imaging protocol provides better image quality than previous compressive imaging schemes. Faster imaging speeds can be attained using this scheme because it requires less data storage space and computing time. Thus, this denoising method offers a very effective approach to promote the implementation of compressive imaging in real-time practical applications.
Osteoporosis is a progressive bone disease, which is characterized by a decrease in the bone mass and deterioration in bone micro-architecture. In theory, photoacoustic (PA) analysis has the potential to obtain the characteristics of the bone effectively. In this study, we try to compare the PA spectral analysis (PASA) method with the quantitative ultrasound (QUS) method in osteoporosis assessment. We compare the quantified parameter slope from the PASA and broadband ultrasound attenuation from QUS among different bone models, respectively. Both the simulation and ex vivo experiment results show that bone with lower bone mineral density has the higher slope in the PASA method. Our comparison study proves that the PASA method has the same efficiency as QUS in osteoporosis assessment.
Flat mirrors, also known as flat parabolic surfaces, for millimeter-wave and terahertz imaging systems are demonstrated. This flat mirror is based on the metasurface in which an inexpensive printed circuit board technology is used to realize copper patterns printed on an FR4 substrate. Compared to the conventional reflector antennas used today in diverse applications (for homeland security, medical systems, communication, etc.), the suggested mirror has major advantages in process simplicity, mechanical flexibility, frequency alignment, weight, and cost. The theoretical background, simulation results, experimental results, and proof of concept are given in this Letter.
Face recognition technology has great prospects for practical applications. Three-dimensional (3D) human faces are becoming more and more important in consideration of the limits of two-dimensional face recognition. We propose an active binocular setup to obtain a 3D colorful human face using the band-limited binary patterns (BBLP) method. Two grayscale cameras capture the BBLP projected onto the target of human face by a digital light processing (DLP) projector synchronously. Then, a color camera captures a colorful image of the human face. The benefit of this system is that the 3D colorful human face can be obtained easily with an improved temporal correlation algorithm and the precalibration results between three cameras. The experimental results demonstrated the robustness, easy operation, and the high speed of this 3D imaging setup.
Several pupil filtering techniques have been developed in the last few years to obtain transverse superresolution (a narrower point spread function core). Such a core decrease entails two relevant limitations: a decrease of the peak intensity and an increase of the sidelobe intensity. Here, we calculate the Strehl ratio as a function of the core size for the most used binary phase filters. Furthermore, we show that this relation approaches the fundamental limit of the attainable Strehl ratio at the focal plane for any filter. Finally, we show the calculation of the peak-to-sidelobe ratio in order to check the system viability in every application.
Metasurface is a new kind of 2D metamaterial that is able to manage a variety of light beam modulations through steering the phase of the scattering waves. In this work, we utilize the metasurface to manipulate the light beam in the mid-infrared regime. By using the metallic rod and the plate structure, the metasurface presents a high polarization conversion efficiency and a wide working bandwidth. With specially rotated metallic rods, the metasurface can realize various light beam manipulations, such as negative reflection, beam collimation, and focusing. All of these results show that such a metasurface will have potential applications in future mid-infrared optics.
The number of layers and the resolution of liquid crystal displays (LCDs) limit the reconstruction fidelity of near-eye light field displays based on multilayer LCDs. Because the eye’s resolution capability is different for central vision and peripheral vision, the fidelity can be improved by setting different weights for different areas. First we employ the eye’s modulation transfer function (MTF) to acquire the limiting resolution angle. Then, due to the inverse relationship between the limiting angle and the weight values, the weighted function related to retinal eccentricity is calculated. In combination with the linear least-squares algorithm, the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of the reconstructed scene is raised. The simulation results indicate that the weighted optimization algorithm can improve the image fidelity and reconstruction accuracy.
Streak tube imaging lidar (STIL) is an active imaging system that has a high range accuracy with the use of a pulsed laser transmitter and streak tube receiver to produce 3D range images. This work investigates the effect of the time bin size on the range accuracy of STIL systems based on the peak detection algorithm. The numerical simulation indicates that the time bin size has a significant effect on the range accuracy, resulting in a modified analytical estimate of the range error. An indoor experiment with a planar target is carried out to validate the theory that shows the linear relationship between the range error and the time bin size. Finer 3D depth images of a fist model are acquired by using a smaller time bin size and the best range error of 0.003 m is achieved with the optimal time bin size of 0.07 ns.
We present the spatial resolution estimation methods for a photon counting system with a Vernier anode. A limiting resolution model is provided according to discussions of surface encoding structure and quantized noise. The limiting resolution of a Vernier anode is revealed to be significantly higher than that of a microchannel plate. The relationship between the actual spatial resolution and equivalent noise charge of a detector is established by noise analysis and photon position reconstruction. The theoretical results are demonstrated to be in good agreement with the experimental results for a 1.2 mm pitch Vernier anode.
In this Letter, we propose an elemental image regeneration method of three-dimensional (3D) integral imaging for occluded objects using a plenoptic camera. In conventional occlusion removal techniques, the information of the occlusion layers may be lost. Thus, elemental images have cracked parts, so the visual quality of the reconstructed 3D image is degraded. However, these cracked parts can be interpolated from adjacent elemental images. Therefore, in this Letter, we try to improve the visual quality of reconstructed 3D images by interpolating and regenerating virtual elemental images with adjacent elemental images after removing the occlusion layers. To prove our proposed method, we carry out optical experiments and calculate performance metrics such as the mean square error (MSE) and the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR).
Correlation imaging is attracting more and more attention as a novel imaging technique taking advantage of the high-order coherence of light fields. To reconstruct an image of the object, many frames of different speckle patterns are required. Therefore, the speed of imaging is strongly limited by the speed of the refreshing rate of the light field. We propose a coprime-frequencied sinusoidal modulation method for speckle pattern creation using a spatial light modulator in a computational ghost imaging system to increase the speed of imaging. The performance of the proposed method is discussed as well.
3D imaging techniques such as computed tomography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging usually combine many scans computationally. Here, we report a 3D imaging approach using an optical-laser diffraction microscope with two different wavelength lasers in the same orientation. A double-layered sample constructed of silica spheres is used for coherent diffraction imaging with two lasers at 543 and 432 nm. The diffraction patterns obtained using a planar detector at a high numerical aperture are projected onto the Ewald spheres. 3D images of the double-layered sample are successfully reconstructed from the two-color spherical diffraction patterns.
High speed pseudorandom modulation and photon counting techniques are applied to a three-dimensional imaging lidar system. The specific structure and working principle of the lidar system is described. The actual detector efficiency of a single-photon detector in an imaging system is discussed, and the result shows that a variety of reasons lead to the decrease in detection efficiency. A series of ranging and imaging experiments are conducted, and a series of high-resolution three-dimensional images and a distance value of 1200 m of noncooperative targets are acquired.
A 38.88 MHz time-stretch line-scan imaging system with parallel interleaving detection is experimentally demonstrated. Since only half-chromatic dispersion is used to stretch optical pulses for wavelength-to-time mapping, the power efficiency is significantly improved by 6.5 dB. Furthermore, the theoretical analysis indicates that the power loss can be efficiently reduced for scan rates less than 100 MHz. In addition, a mathematical model for signal-to-noise evaluation is derived, including amplified spontaneous emission noise in the power compensation. Thanks to the improvement of the power efficiency by using parallel interleaving detection, the signal quality is enhanced.
Noise and the resonance characteristics of the focal plane array (FPA) are the most important factors that affect the performance of the optical readout infrared (IR) FPA imaging system. This Letter presents a time-discrete modulation technology that eliminates the background and restrain noise, which effectively improves the image quality of the optical readout IR FPA imaging system. The comparative experiments show that this technology can reduce the noise equivalent temperature difference greatly and make the images sharper. Moreover, when the imaging system is influenced by the environment vibration, the images obtained from the imaging system with time-discrete modulation restore twice as fast as without time-discrete modulation.
A practical millimeter-wave (MMW) holographic imaging system with good robustness is developed for the detection of concealed weapons at security checkpoints, especially at the airport. The system is used to scan the passenger and detect any weapons hidden in their clothes. To reconstruct the three dimensional image, a holographic MMW imaging algorithm based on aperture synthesis and backscattering is presented. The system is active and works at 28–33 GHz. As a practical imaging system, the robustness is analyzed in detail in terms of the peak signal-to-noise ratio.
We present an improved compressive sensing algorithm with negative transformation and piecewise-nonlinear transformation. The reconstruction characteristics of the improved algorithm are studied by conducting numerical analysis research. Watch gear and handwritten character are used in the experiments. The results validate the application value of the improved algorithm in improving 2D reconstructed image quality in terahertz (THz) Gabor inline digital holography.
We present a method of time coding with ABAB synchronization timing control for real-time 3D super-resolution range-gated imaging (3DSRGI). To meet the high precision of time delay and pulse width in ABAB synchronization time sequencing, phase shift is implemented to achieve ns-scaled delay and width accuracy without restoring to high clock frequencies. Theoretical analysis and experiments prove that 1 ns delay and width precision is obtained by our timing control unit based on a single field-programmable gate array with 5 ns clock cycle. Finally, a prototype experiment of 3DSRGI is demonstrated at a 10 Hz video rate with 696 pixels×520 pixels.
For manufacturing a fine optical glass lens, it is important to obtain a 3D profile of a semi-finished product with a rough surface. We develop an active binocular 3D scanning setup to measure the 3D profile of a rough surface optical element. Two cameras simultaneously capture the band-pass binary random patterns which are projected on the target object. The highlight of this system is using the temporal correlation technique to determine the stereo correspondence between the pixels of the two cameras. The 3D point cloud can be reconstructed by the triangulation principle. Experiment results confirmed that this method effectively measures the rough surface of an optical element with sufficient accuracy.
This Letter proposes a high bit-depth coding method to improve depth map resolution and render it suitable to human-eye observation in 3D range-intensity correlation laser imaging. In this method, a high bit-depth CCD camera with a nanosecond-scaled gated intensifier is used as an image sensor; subsequently two high bit-depth gate images with specific range-intensity profiles are obtained to establish the gray depth map and finally the gray depth map is encoded by an equidensity pseudocolor. With this method, a color depth map is generated with higher range resolution. In our experimental work, the range resolution of the depth map is improved by a factor of 1.67.
In this Letter the problem of optimization of speckle patterns in a ghost imaging (GI) system is addressed. The mutual coherence between the measuring matrix and the sparsifying dictionary matrix is minimized to obtain the required speckle patterns. Simulation and experimental results are presented, both showing that the quality of the reconstructed results obtained with the optimized speckle patterns is much improved in comparison with that obtained with the general unoptimized ones. We expect this method can be used to design GI systems with high performance.
In this Letter, we propose a three-dimensional (3D) image reconstruction method with a controllable overlapping number of elemental images in computational integral imaging. The proposed method can control the overlapping number of pixels coming from the elemental images by using the subpixel distance based on ray optics between a 3D object and an image sensor. The use of a controllable overlapping number enables us to provide an improved 3D image visualization by controlling the inter-pixel interference within the reconstructed pixels. To find the optimal overlapping number, we simulate the pickup and reconstruction processes and utilize the numerical reconstruction results using a peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) metric. To demonstrate the feasibility of our work in optical experiments, we carry out the preliminary experiments and present the results.
A surface defect evaluation system can combine microscopic scattering dark-field imaging with sub-aperture scanning and stitching. Thousands of sub-apertures are involved; mechanical errors will cause stitching dislocation, leading to defect cracks. In this Letter, we propose standard line coordinate error adjustment dealing with consistency error between coordinates of the scanning and imaging system, and defocus depth estimation leveling method dealing with high-cleanliness fine optics defocuing caused by the surface which is not perpendicular to microscope’s optical axis. Experiments show defect cracks are effectively solved and the defocus of 420 mm×420 mm components can be controlled within depth of field 20 μm.
The stochastic parallel gradient descent (SPGD) algorithm is widely used in wavefront sensor-less adaptive optics (WSAO) systems. However, the convergence is relatively slow. Modal-based algorithms usually provide much faster convergence than SPGD; however, the limited actuator stroke of the deformable mirror (DM) often prohibits the sensing of higher-order modes or renders a closed-loop correction inapplicable. Based on a comparative analysis of SPGD and the DM-modal-based algorithm, a hybrid approach involving both algorithms is proposed for extended image-based WSAO, and is demonstrated in this experiment. The hybrid approach can achieve similar correction results to pure SPGD, but with a dramatically decreased iteration number.
We propose a novel method of slice image reconstruction with controllable spatial filtering by using the correlation of periodic delta-function arrays (PDFAs) with elemental images in computational integral imaging. The multiple PDFAs, whose spatial periods correspond to object’s depths with the elemental image array (EIA), can generate a set of spatially filtered EIAs for multiple object depths compared with the conventional method for the depth of a single object. We analyze a controllable spatial filtering effect by the proposed method. To show the feasibility of the proposed method, we carry out preliminary experiments for multiple objects and present the results.
An angular trapezoidal phase mask used for a wideband coronagraph is proposed. The azimuthal phase of the mask is double-periodic and has both trapezoidal and constant parts in each period. This kind of continuous phase distribution can be employed to avoid the abrupt phase variation of the 6-level phase distribution we proposed previously. Numerical calculations show that this more practical phase mask can still keep its superior performance in terms of starlight elimination, small inner working angle, and good achromatism. It is of great importance that there is no singularity in this kind of mask except for a singularity at the center. This mask design is close to real manufacturing conditions, and the process technology is superior.
Photoacoustic imaging with a synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT) is an effective method to improve the lateral resolution for out-of-focus regions in scanning microscopy systems, which commonly require a decent motorized scanning stage for a lateral scan of a transducer to obtain a cross-sectional image. In this study, we propose and test a photoacoustic imaging system with a scanning mirror-based SAFT (SM-SAFT) for simple and fast data acquisition, without the need for a physical scan of the transducer. Photoacoustic images of hair phantoms acquired by SM-SAFT are demonstrated, serving as a proof-of-concept experiment to show the feasibility and potential of the proposed approach.
Adaptive optics is implemented in a confocal scanning fluorescence microscopy using a wavefront sensorless correction scheme. Using the image sharpness as the optimization metric, aberration correction is performed to compensate both system- and specimen-induced aberrations by using stochastic parallel gradient descent algorithm based upon Zernike polynomial modes. We demonstrate the idea of using phantom fluorescence samples experimentally. Enhanced imaging contrast and improved signal level are achieved.
Laser generation and electromagnetic acoustic transducer (EMAT) detection techniques are combined as a hybrid ultrasonic technique for the inspection of the defects in the steel. Laser transmits through the optical fiber and irradiates on the steel surface. In case of inspection, Rayleigh wave is generated to test the surface defects based on the principle of mode conversion. In order to improve the testing accuracy and signal-to-noise ratio, wavelet soft-threshold method is introduced in the present work. Experimental results show that errors of testing surface defect are less than 10%, which proves laser-EMAT technique to be suitable for nondestructive assessment of metallic materials.
There is a need to develop a non-destructive and fast detection method for bruising of fruits because the injuries lower quality of fruits, which lead to economic loss. In this paper, we propose a method to detect the bruise on apple surface with hyperspectral imaging technique. A hyperspectral image system consisting of a CCD digital camera, a line scanning spectrometer and a movable platform is designed to acquire the hyperspectral images of injured apples. Two models are established to distinguish the injured area on the surface from the normal area based on image processing technique with spatial clustering and Spectral Angle Mapper Classification (SAM), respectively. The discrimination accuracy of the SAM model is up to 100%, which is much higher than the spatial clustering model.
DNA tetrahedral nanostructures are considered to be new nanocarriers because they can be precisely controlled and hold excellent penetration ability to the cellular membrane. Although the DNA tetrahedral nanostructure is extensively studied in biology and medicine, its behavior in the cells with nanoscale resolution is not understood clearly. In this letter, we demonstrate superresolution fluorescence imaging of the distribution of DNA tetrahedral nanostructures in the cell with a simulated emission depletion (STED) microscope, which is built based on a conventional confocal microscope and can provide a resolution of 70 nm.
We demonstrate a series of experiments on imaging through both stationary aberrating media and moving aberrating media by computational ghost imaging (CGI). An incoherent LED light source is used instead of the common pseudothermal light source (laser light passing through a rotating ground glass). A digital micromirror device is used as a simple spatial light modulator to perform CGI. Moreover, a digital filtering method is introduced to improve imaging quality through moving aberrating media. This imaging modality may have potential applications in medicine and astronomy.
We propose an integral imaging system that uses three lens arrays, including two convex lens arrays and a concave lens array. Compared with the conventional integral imaging system, the proposed system can remarkably enhance the viewing angle. The maximum viewing angle can be enlarged to 48o, which is 4.8 times wider than that of the conventional system. The principle of the proposed system is elucidated, and the experimental results are presented in this letter.
A novel laser-electro magnetic acoustic transducer (EMAT) system for nondestructive testing NDT surface crack of continuous casting billet (CCB) is provided. Rayleigh wave generated by line laser source is used to detect the surface crack of CCB. According to the principle of mode conversion from Rayleigh wave to shear wave, the defect signal is received using the shear wave EMAT sensor in a non-contact way. Experiments are carried out on the steel sample with size 30 × 0.2 × 0.2 (mm) of crack. Further, the influences of life off value and distance between EMAT sensor and laser beam on the testing sensitivity are discussed, respectively. It is found that the life off value is the main factor that effects sensitivity of the proposed method. There is a clear prospect of the method applied to test continuously cast bloom at high temperature.
In this letter, a new single three-dimensional (3D) laser projector is proposed. As liquid crystal (LC) can produce two image patterns with orthogonal polarization states at 120 Hz, only one projector is required in this approach for reconstruction of a 3D object. The light source is made up of RGB (red, green, and blue) lasers because laser has lots of advantages such as longer life, higher brightness, and larger color gamut. A novel diffusive media with good polarization-maintaining quality is used as rear projection screen for its high transmission efficiency (~90%) and low reflection efficiency. When laser incidents into the diffusive media, which contains lots of spherical particles with sizes between 2 and 15 \mu m, laser is scattered randomly and the laser speckle is reduced. A spatial phase mask is also inserted into the optical path to reduce speckle. With these techniques, the speckle contrast is reduced to 0.1 and the quality of image patterns has been greatly improved.
Infrared thermography determines the surface temperature of an object or human body. It is a promising imaging technology for medical and biological observations due to its contactless and completely noninvasive properties. However, traditional two-dimensional (2D) infrared thermography cannot retain the spatial information, and thus provides only qualitative diagnosis information. A novel real-time three-dimensional (3D) infrared imaging system which takes full advantages of high-speed, high-quality, high-sensitivity, and low-cost in 3D thermograph is presented. We demonstrate the real-time 3D thermal imaging at the speed of 24 frames per second (fps), with resolution of 640 \times 480 points. Experimental results demonstrate quantitatively measurement of temperature distribution of 3D surfaces in real-time is realized with this system.
A crosstalk-free integral imaging display consisting of a display panel and double plano-convex micro-lens array is proposed. The double plano-convex micro-lens array includes two micro-lens arrays, A and B. Micro-lens array A is used to eliminate crosstalk by completely reflecting crosstalk lights. Micro-lens array B, located near micro-lens array A, is used to display three-dimensional images. Computer simulations based on ray-tracing are conducted. Crosstalk-free reconstruction images may be clearly observed from the simulation results.
To meet application requirements of high resolution and high frame rate for the aerial camera, a real-time high definition (HD) aerial camera imaging system is designed and developed. A KAI-01050 charge-coupled device (CCD), ADSP-BF561, and AD9920A are used in the system. ADSP-BF561 is used to configure registers of AD9920A for generating the timing-driven signals to meet CCD parameter needs, and image stitching through ping-pong operation of collected video signals is achieved, then the image is displayed correctly. In the end, the system is developed, 1 M pixels and 60 frame rate are realized, and running results on the system verify effectiveness of the design program.
Polarization aberration of optical systems in imaging polarimetry affects the polarization detection accuracy, especially in wide field of view and large relative aperture systems. The polarization aberration of the imaging lens in imaging polarimetry is demonstrated and analyzed through the way of polarization ray tracing. The impact of polarization aberration on the polarization detection accuracy of imaging polarimetry is also discussed. The variation of Stokes parameters as functions of the field of view and the relative aperture is achieved. The polarization aberration can be reduced and calibrated at different field of view and the relative aperture of the optical systems, and the correct polarization information of the object can be derived.
The third-order ghost imaging with the second-order intensity correlation is theoretically and experimentally demonstrated. The resolution and visibility of the reconstructed image are discussed, and the relationship between resolution and visibility is analyzed. The theoretical results show that a tradeoff exists between the visibility and resolution of the reconstructed image; the better the image resolution, the worse the image visibility. Numerical simulations are carried out to verify this theory, and a ghost imaging experiment is conducted to validate our calculations. The experimental results agree with the theoretical predictions.
The deviation caused by acousto-optic tunable filter (AOTF) diffraction in multispectral imaging is analyzed through derivation calculus of the deviation angle. The rotatory polarization of acousto-optic crystal is taken into account in this analysis. The relationships between the polar angle of the incident and the diffracted beams are acquired by using the momentum-matching condition. During the diffraction of the incident beams, far more deviations are induced.
Distance resolutions and noises are analyzed experimentally for long-range three-dimensional (3D) active imaging systems that have signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) more optimal than 30:1. Findings indicate that the photon shot noise primarily determines the SNR. However, the active imaging method, which has a relatively low SNR, generates a relatively high distance resolution. To explain this phenomenon, a theory in which the distance resolution of 3D active imaging systems is determined by both the photon shot noise and the subinterval width is developed. Theoretical and experimental results differ by less than 4%.
We present an image recognition method to distinguish targets with cat-eye effect from the dynamic background based on target shape and modulation frequency. Original image sequences to be processed are acquired through an imaging mechanism that utilizes a pulsed laser as active illuminator and an industrial camera as detection device. There are two criterions to recognize a target: one exploits shape priors and the other is the active illuminator’s modulation frequency. The feasibility of the proposed method and its superiority over the single criterion method have been demonstrated by practical experiments.
We propose a new analytical edge spread function (ESF) fitting model to measure the modulation transfer function (MTF). The ESF data obtained from a slanted-edge image are fitted to our model through the non-linear least squares (NLLSQ) method. The differentiation of the ESF yields the line spread function (LSF), the Fourier transform of which gives the profile of two-dimensional MTF. Compared with the previous methods, the MTF estimate determined by our method conforms more closely to the reference. A practical application of our MTF measurement in degraded image restoration also validates the accuracy of our model.